
Your financial future can be much affected by your choice between National Pension System (NPS) and Public Provident Fund (PPF). Across important criteria, this thorough analysis lets you decide wisely based on your own requirements and objectives by means of both investment opportunities.
PPF and NPS Overview
PPF
The Public Provident Fund is a governmentsupported longterm savings plan with tax benefits that delivers guaranteed returns. PPF, introduced in 1968, seeks to encourage small savings and offer retirement protection to selfemployed people and workforce in the informal economy.
NPS.
Created to allow systematic savings during your working years, the National Pension System is a voluntary, defined contribution retirement savings system. Though originally for public employees, NPS is now open to every Indian between 18 and 70 years of age.
Investing structure and operating behavior
PPF Composition
- Account Variety: a private account that may not be jointly maintained
- Government of India legislative bodyApowered
- Minimum Annual Investment: 500 Indian rupees.
- A maximum capital of ₹1,50,000 per year.
- Fifteen-year maturity period with increments of five years for extension choices
- Post offices and authorized banks offer account opening opportunities
Structure of NPS
- Account Type: Tier I (mandatory, limited withdrawals) and Tier II (optional, flexible withdrawals)
- Control Authority: Legislationssec PFRDA (Pension Fund Control and Development Authority)
- Tier I accounts have a minimum investment of ₹500 and Tier II accounts have one of ₹1,000.
- Maximum Investment: No upper constraint
- With options to go upstream until 70, the investment cycle finishes at retirement age—60 years.
- By means of banks, online sites, or NPS service suppliers, assist opening holder with a.
You May Like to Read: How to Become an Income Tax Officer
Risk level and returns
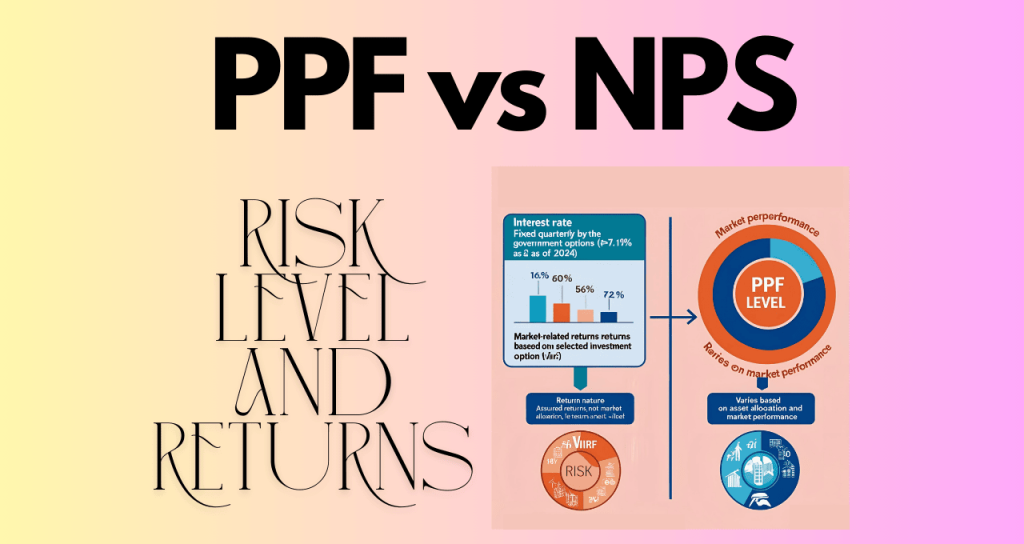
| Parameter | PPF | NPS |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rate | Fixed quarterly by the government (~7.1% as of 2024) | Market-related returns based on selected investment option |
| Return Nature | Assured returns, not market-dependent | Varies based on asset allocation and market performance |
| Risk Level | Virtually risk-free (government-backed) | Low to moderate risk depending on the chosen fund |
| Historical Performance | 7-8% annually over the last decade | Equity funds: 10-12% annual returns; Government securities: 8-9% |
Investment options and flexibility
PPF Structure
- Account variety: Personal account which could not be jointly maintained.
- Government of India legislative body regualtes.
- Minimum Yearly Investment: ₹500
- Maximum yearly investment: ₹1.5 million
- Maturity Period: 15 years followed by optional fiveyear extensions.
- Account opening is possible via authorized banks and post offices.
Organization of NPS RUNS
- Otherwise referred to as: Tier one, which has to do with limited distributions,
- Level II: discretionary, flexible withdrawal
- Controlling Authority: PFRDA (Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority)
- ApiController’s Minimum Investment: Level one: ₹500
- Tier 2: 1000 rupees
- Maximum Investment: No upper limit.
- Until retirement age of 60, with possible extension to 70 years, investment duration:
- Bank accounts, internet portals, or NPS service providers are available
Tax credits and results

PPF Tax Relief
- An ideal $1,50,000 tax break under Section 80C is possible by means of investment phase contributions.
- Interest gained is totally free of taxes in accumulation phase.
- Withdrawal Other: Maturity sum (principal and interest) entirely free of tax
- Tax Status: Enjoys EEE (ExemptExemptExempt) status across all three phases.
NPS tax advantages
Investment Phase:
- Up to ₹1,50,000 deduction under Section 80C
- Additional ₹50,000 deduction under Section 80CCD(1B)
- Employer contributions up to 10% of salary (basic + DA) deductible under Section 80CCD(2)
Accumulation Phase: No tax on growth
Withdrawal Phase:
- 60% of corpus is tax-free at maturity
- 40% must be used for annuity purchase (taxable as per income slab)
Tax Status: EET (Exempt-Exempt-Taxed)
You May Like to Read: Tax Concept - Complete Guide
Liquidity and Withdrawal Terms
PPF Liquidities Properties
- Lockin duration: 15 years (with fiveyear extensions)
- From 7th year forward, partial withdrawals are permitted.
- 50% maximum balance at the end of the 4th year or just before year four.
- Allowed for certain cases such as medical emergencies or advanced education five years inact in particular.
- Extension Choices: Can be extended in 5year increments ad infinitum after maturity.
NPS liquidity characteristics
- Before age 60, a lockin period applies.
- Partial Removals:
- Let funds for particular needs (marriage, home purchase, higher education, medical treatment) represent up to 25% of their own contributions.
- maximum of three draw during entire tenure
- Except for serious illness, at least five years should pass between draws.
- Minimum 80 percent of corpus must be spent on annuity across first 60 decades
- At 60 years old, at least 40% of corpus should be spent on annuities.
- Option for deferment: Withdrawal can be postoned up to 70 years of age.
Nomination and Inheritance
| Parameter | PPF | NPS |
| Nominee Facility | Available when account opened or thereafter | Compulsory upon registration |
| Multiple Nominees | Can appoint several nominees with particular shares | One can name up to three with particular shares |
| Legal Heirs | Follow intestate laws in absence of will | If there is no valid nomination, legal heirs inherit based on laws of succession |
| Death Benefit | Whole balance given to legal heirs/nominees | Options for death benefit are lump sum withdrawal or annuity purchase by beneficiaries |
Operating Freedom
PPF Operational Characteristics
- Account Management: Straight passbook based approach
- Online Access: Limited online availability depending on the bank.
- Transaction processes using online transfers, check, or money.
- Documentation: Operations need only minimal documents.
- Via particular bank or post office avenues, grievance redressal
NPS operational attributes
- Account Management: system controlled by PRAN
- Online access: full online account management servicesWorks
- Methods of transaction: electronic transfers, autodebit options.
- Documentation: Larger amounts of documentation than PPF.
- Grievance Redressal: Threetier grievance redressal framework
Perfect investor profile

Who ought to pick PPF?
- For risk appetite: Conservative investors looking for sure returns.
- Income Level: Middle to low net worth individuals.
- Objective of investing: preservation of capital.
- Age Group: Good for all age groups, particularly older than 45 years in search for safe investments.
- For those without employer retirement benefits and selfemployed people, this is especially helpful.
Who should select NPS?
- Risk appetite: Old propensity taken allow marketlinked return
- income Level: Middle to upper Class folk
- Financial Objective: Longterm retirement plans yielding good returns.
- Age Group: Particularly beneficial for early investors (2540 years) who can take advantage of longterm equity exposure.
- For both salaried (extra tax benefits on employer contribution) and selfemployed people, employment status is advantageous.
Pro/Con Outline

PPF Benefits
- Government-guaranteed, totally safe investment
- Fully taxexempt throughout all stages of life (EEE status)
- Fixed returns irrespective of market circumstances.
- Easy to run and grasp
- Flexible contribution levels within permitted bounds
- Opportunity to while extend in 5year increments after maturity
- A few disadvantages of PPF
- Lower return potential relative equitylinked choices
- 15year lockin period
- limited investment level ($150,000 yearly)
- No leeway in distributing assets.
- No chance to take advantage of rises in the stock market.
NPS Benefits
- Opportunity for better yields from equity exposure
- tax advantages going beyond Section 80C limit
- Highly versatile investing choices
- Respectable fund management with reasonable prices.
- Mobile account spanning businesses and geographies.
- Normal account statements and straightforward composition
- Disadvantages of NPS:
- Returns not certain; exposed to market volatility
- Only partial tax exemption at withdrawal (qualified for EET)
- Compulsory purchase of annuities (40% of portfolio)
- Other investing opportunities have more liquidity
- More sophisticated with many fund choices could be the structure.
Comparative Analysis B/W PPF and NPS
| Parameter | PPF | NPS |
|---|---|---|
| Returns | Fixed (7.1% currently) | Market-linked (potentially 8-12%) |
| Risk | Virtually nil | Low to moderate |
| Lock-in Period | 15 years | Until age 60 |
| Maximum Investment | ₹1,50,000 per year | No upper limit |
| Tax Benefits | EEE (fully tax-exempt) | EET (partial taxation at withdrawal) |
| Liquidity | Partial withdrawals from 7th year | Limited partial withdrawals (25%) after 3 years |
| Fund Management | Government managed | Professional fund managers |
| Investment Flexibility | None | Multiple asset classes and allocation strategies |
| Loan Facility | Available | Not available |
| Exit Options | Lump sum withdrawal at maturity | 40% mandatory annuity purchase |
Practical Factors Will Help You Decide
Using both alternatives allows us to$row.flushurious.
To strike a balance between safety and growth, several financial professionals advocate for keeping both NPS and PPF accounts. Think of apportioning money based on:
Your age together with your retirement period is three years.
- Total attitude to risk
- Elsewhere in your portfolio are other assets.
- Tax preparation requirements
Stage in your life
- Early Career (25-35 years): More of NPS with equity emphasis for longterm growth
- MidCareer (35-45 years): Equilibrated strategy including PPF and NPS.
- Late in career (45+ years): More PPF allocation for capital maintenance
Particular financial objectives
- PPF is better for guaranteed returns and complete safety—a fact.
- Better opportunities will come from some market exposure leading to possibly better returns: NPS.
- Optimal tax advantages result from a combination.
In essence, what alternative would you pick?
Choose PPF whether:
- Your top priority is guarding principal.
- You seek total tax exemption in every phase of life.
- You like straightforward investment options that require little supervising.
- After 7 years, you could want access to money.
- You are close to retirement and require definite yields
Select NPS provided
- You are concentrating on creating a retirement fund with possible higher yields.
- You hope for asset distribution according to age and level of risk tolerance.
- You’re searching for more tax savings over the Section 80C limitation.
- Your investment time frame is long; you have at least twenty years prior to retiring.
- You are looking for professionally handled funds at a low price.
A balanced strategy using both tools in many circumstances offers an ideal mix of returns, security, and tax efficiency adjusted for your specific financial situation and goals.
